Filter
50 products
Type: Nursing
3M Micropore Surgical Tape Box
Type: Nursing
Uro Bag Romo 10 DB-1070-10 (Pack of 10)
Type: Nursing
SafeCath Silicon Two Way Foleys Cathete
Type: Nursing
Mackintosh Sheet Mattress Protector for Bed (10m)
Type: Nursing
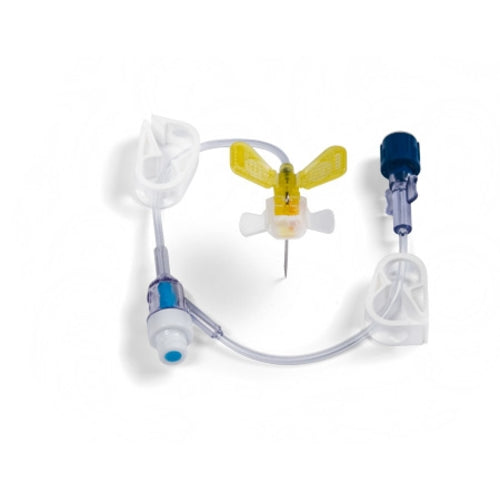
BARD Winged Infusion Set
Type: Nursing
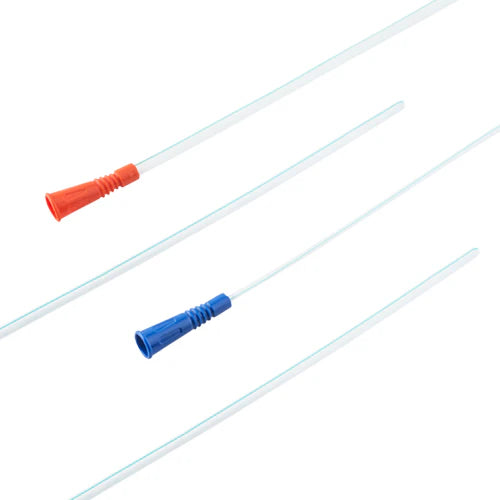
Nel Cath GS 1004
Type: Nursing
JMS Medi Tape Micropore Dressing
Type: Nursing
Yankur Suction Set Handle with 2Mtr Tubing
Type: Gauzes
Sterile Gauze 12 Ply Swab Dressing (100 Pc - 25 packs of 4 Each)
Type: Nursing
Gauze Than 90cm x 18mtr (1 than)
Type: Nursing
Karman type Cannula with Adaptor (pack of 25)
Type: Nursing
BD Discardit II Syringe 20ml (Pack of 80)
Type: Nursing
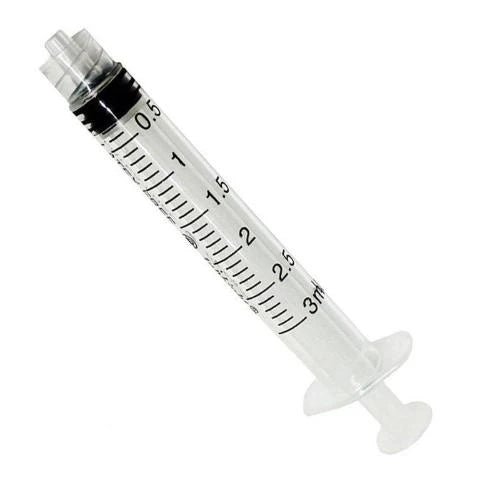
BD Syringe 3ml Luer Lock (Pack of 100)
Type: Nursing
BD Luer-Lock Syringe 10ml (Pack of 100)
Type: Nursing
Umblical Cord Clamp Sterile (Pack of 100)
Collection:
Nursing
Essential nursing products
Nursing keeps care safe, simple, and human. Nurses bridge doctors, families, and patients. They set up lines, dress wounds, give injections, and watch every small change. Because every minute matters, they need nursing supplies that work the first time and keep working all day. Therefore, this Nursing collection brings together essential nursing products and small nursing equipment for quick, steady workflows at the bedside, in wards, and in home care. Moreover, for maternal and neonatal needs, we also include solutions that complement a supplemental nursing system, so breastfeeding support remains practical and safe in real settings.
Moreover, we focus on practical choices with clear labeling, clean packaging, and consistent performance. You will find winged infusion sets, syringes, catheters, gauze, umbilical cord clamps, Karman cannulas, and related nursing supplies. These nursing products are the backbone of safe IV access, drug delivery, wound care, and obstetric support. Consequently, teams can stock fast, train fast, and care with confidence. Key models on your collection include BARD Winged Infusion Set, BD Syringes (3 ml, 10 ml, 20 ml Discardit II), Sterile Gauze Swab 12-ply, Gauze Than rolls, Umbilical Cord Clamp (sterile), Karman-type cannula with adaptor, and Nel Cath GS 1004. In parallel, lactation teams can pair consumables with a supplemental nursing system where indicated, which adds flexibility without disrupting routine nursing equipment and protocols.
Why This Nursing Collection Matters
Even simple tasks carry risk if tools fail. Hence, dependable nursing products reduce errors, shorten procedures, and prevent avoidable waste. With standardized SKUs and trusted brands, nurses can reach for the right size and finish the task without delay. Furthermore, clear IFUs and sterile packs help new staff learn safely. When lactation is involved, a supplemental nursing system can support continuity of feeding while keeping the workflow aligned with existing nursing equipment.
Because costs and availability affect care, we also group high-rotation nursing supplies and offer value packs where suitable. As a result, stores can plan budgets, and wards can maintain steady PAR levels without last-minute stockouts. In addition, aligning nursing products with maternal-newborn needs — including optional supplemental nursing system components — keeps purchasing simple and consistent.
Core Nursing Use-Cases
1) IV Access & Medication Delivery
Winged infusion sets provide gentle venipuncture, especially for fragile veins or short-term lines. The flexible wings and thin-wall needles help stabilize entry and reduce movement. Your collection features BARD Winged Infusion Set for reliable access and accurate flow. These are foundational nursing supplies that integrate smoothly with routine nursing equipment.
Syringes are essential for injections, flushes, and accurate dosing. Because sizes vary by drug and route, we stock common volumes: BD 3 ml Luer Lock, BD 10 ml, and BD Discardit II 20 ml for dilution, irrigation, and medication pushes. Luer-lock designs add security during connection, which keeps nursing products consistent and safe shift after shift.
2) Wound Care & Dressing
Sterile Gauze 12-ply swabs are the mainstay for absorption, cleaning, and packing. They help manage exudate and maintain a clean field. Consequently, these nursing supplies keep procedures efficient.
Gauze Than (90 cm × 18 m) supports bulk dressing prep, padding, and secondary layers. It also helps optimize costs in high-volume wards. Thus, stores can align nursing equipment trays with predictable usage.
3) Urology & Catheterization
Nelaton catheters (e.g., Nel Cath GS 1004) support intermittent bladder drainage and short procedures. Smooth tips and consistent sizing ease insertion and reduce trauma when used correctly. Therefore, these nursing products remain staple items across general wards.
4) Obstetric & Gynecology Support
Umbilical cord clamps (sterile) ensure quick, secure clamping to prevent blood loss in newborns. Consistent locking teeth help maintain hold until cord separation. Meanwhile, for breastfeeding support, a supplemental nursing system can be introduced by trained staff to stabilize feeding while maintaining skin-to-skin care.
Karman-type cannulas with adaptor support uterine evacuation procedures in approved settings. Smooth cannula profiles and compatible adaptors help maintain seal and reduce leakage. Consequently, these nursing supplies align well with established nursing equipment kits and checklists.
Product Highlights
- BARD Winged Infusion Set – Stable wings, predictable flashback, and easy taping for short procedures and day-care infusions. Moreover, the thin-wall design supports good flow with smaller gauge sizes. These are reliable nursing products for fast IV access.
- BD Syringe 3 ml Luer Lock – Ideal for IV meds and flushes where a firm lock is vital. Additionally, gradations are clear, which improves dosing accuracy. Therefore, it’s a core piece of nursing equipment.
- BD Luer-Lock Syringe 10 ml – Versatile size for reconstitution and gentle irrigation. Therefore, it reduces the number of SKUs needed for routine work across your nursing supplies list.
- BD Discardit II 20 ml – Useful for larger volume flushes, wound irrigation, and dilution steps. As a result, tray setups become simpler and more consistent with standard nursing products.
- Sterile Gauze 12-ply Swab – Soft hand-feel, good absorbency, and clean edges reduce lint. Consequently, dressing changes stay tidy with dependable nursing supplies.
How Nurses Use These Items (Step-By-Step)
A) Starting a short infusion
- Verify order, allergies, and access site.
- Prime line; prepare BARD winged infusion set. Then clean skin with approved antiseptic.
- Insert at low angle; confirm flashback; secure wings with tape.
- Connect line or syringe; set rate; monitor site and patient response.
(These steps rely on standardized nursing products and stable nursing equipment.)
B) IV medication push with Luer-lock syringe
- Check drug, dose, dilution, and rate.
- Draw with BD syringe; expel air; relabel if required.
- Confirm patency; push at the recommended rate; flush line.
- Document time, dose, site condition, and patient tolerance.
(Using the right nursing supplies keeps documentation clean and consistent.)
C) Dressing a clean wound
- Wash hands; open sterile gauze packs; prepare normal saline if needed.
- Gently clean and pat dry; apply primary dressing; add gauze than as secondary layer.
- Secure with tape or bandage; label with date and initials; educate patient on signs of infection.
(Aligned nursing equipment and nursing products reduce waste and rework.)
D) Cord clamping in delivery
- After safe delivery and delayed clamping as per protocol, apply sterile umbilical cord clamp close to the neonate.
- Verify lock; trim cord; recheck hemostasis; monitor mother and baby.
(If indicated later, a supplemental nursing system can support breastfeeding while keeping workflow steady.)
Stocking Strategy for Nurse Managers
- Standardize sizes to reduce picking errors. Keep common syringe volumes (3 ml, 10 ml, 20 ml) and a small set of winged infusion gauges for adult and pediatric use. This keeps core nursing supplies aligned across shifts.
- Label shelves with color codes matching package labels for quicker pulls.
- Build procedure trays for venipuncture, dressing change, and cord care. Then restock after each shift to keep nursing equipment consistent.
- Rotate inventory first-in, first-out to protect sterility and avoid expiry.
- Document consumption to forecast monthly PAR levels and prevent stockouts during peak census. Therefore, your nursing products plan remains stable and predictable.
Buyer’s Guide
- Infusion sets: pick gauge by vein size and therapy duration. Smaller gauge means gentler entry yet slower flow; thus, select nursing products to match protocols.
- Syringes: choose Luer-lock for pressurized connections; choose appropriate volume to improve dosing accuracy. This keeps nursing equipment safe and steady.
- Gauze: use sterile swabs for open wounds; keep bulk rolls for padding and secondary dressings; integrate with high-rotation nursing supplies.
- Catheters (Nelaton): match French size to patient and indication; use sterile technique and lubrication.
- Cord clamp: verify sterile pack and locking action before use; after delivery, consider whether a supplemental nursing system is indicated for feeding support.
- Karman cannula: confirm compatibility and follow institutional protocols so nursing products remain compliant and easy to audit.
Why choose MeddeyGo?
MeddeyGo simplifies nursing by curating high-rotation nursing supplies.
Moreover, we keep nursing products ready to ship with clear specs and fair pricing.
We partner with hospitals, clinics, and home-care teams across India.
Therefore, packaging is clean, sizing is true, and selection stays simple.
You’ll find BARD winged infusion sets, BD syringes, and core gauze formats.
Additionally, we stock Nelaton catheters, cord clamps, and Karman-type cannulas.
Standardization matters, so trays stay consistent and errors drop.
Consequently, safety improves every day with familiar nursing equipment.
Our pages use plain, clinical language.
Thus, nurses quickly compare sizes, connectors, and sterility—and reorder fast.
Inventory is visible; packaging is professional; shipping is prompt.
As a result, nursing supplies reach shelves on time with less wastage.
We align to recognized standards and show model names for QA.
Hence, audits move faster, and scaling—via PAR planning—stays smooth.
Finally, we focus on people first.
Because of this, the site is simple, support is quick, and nursing products deliver real results.
FAQ
What are the most essential nursing consumables to stock first
Start with IV access and medication delivery tools, since they are used hourly: winged infusion sets, 3 ml / 10 ml / 20 ml BD syringes, and standard flush supplies. Next, add sterile gauze swabs and gauze rolls for dressing changes. Then include catheters and umbilical cord clamps based on your ward mix. This order keeps high-frequency nursing products always available and aligned with core nursing equipment.
When should I use a winged infusion set instead of a standard cannula?
Choose winged infusion sets for short infusions, blood draws, or fragile veins. The wings help stabilize the needle and reduce movement at the entry point. For longer therapies, consider a peripheral IV cannula per protocol. Always follow aseptic technique and secure with tape. In every case, select nursing products that match your unit’s guidelines.
What makes 12-ply sterile gauze useful in daily care?
It absorbs well, handles cleaning without shredding, and comes in sterile packs that protect wounds. Use it for dressing changes, minor procedures, and post-op care. Keep gauze than rolls for padding and secondary layers to optimize costs. Thus, your nursing supplies stay efficient and predictable.
Which Nelaton catheter size should I pick?
Select French size as per patient and indication. Use adequate lubrication, maintain aseptic technique, and secure drainage correctly. Because sizes on listings are true to label (e.g., Nel Cath GS 1004), you can standardize by protocol. Dispose of single-use nursing products safely after use.
Are umbilical cord clamps single-use?
Yes. They are sterile and designed for one-time use at delivery. Check the lock, listen for the click, and confirm hemostasis. Then monitor the neonate and follow your unit’s cord-care protocol. If breastfeeding support is needed, a supplemental nursing system may be introduced later by qualified staff.
Can I request bulk-order pricing or brand equivalents?
Yes. MeddeyGo supports bulk and tender queries. We can also map near-equivalent models if your formulary changes. Because documentation matters, we keep model names visible for fast verification. Contact support for quotes and lead times on core nursing equipment and high-rotation nursing supplies.
Do you help with standardizing trays?
We can suggest a practical set of sizes and SKUs for IV starts, dressing changes, and cord care. Then you can label shelves and set PAR levels. This approach reduces picking errors and speeds up end-of-shift restocking. Consequently, your nursing products and nursing equipment remain consistent across shifts.
MeddeyGo CTA
Ready to stock dependable nursing supplies? Explore winged infusion sets, BD syringes, sterile gauze, gauze rolls, Nelaton catheters, umbilical cord clamps, and Karman cannulas in one place—delivered fast across India. Shop the full Nursing collection on MeddeyGo today. For lactation pathways, plan your kits so they work smoothly alongside a supplemental nursing system and standard nursing equipment.
| Sub-Category | Typical Uses | Key Features | Popular Models on Page |
|---|---|---|---|
| Winged Infusion Sets | Short infusions, blood draws, fragile veins | Stabilizing wings, thin-wall needle, easy taping | BARD Winged Infusion Set |
| Syringes (Luer-Lock) | Drug delivery, line flushes, reconstitution, irrigation | Secure lock, clear markings, common volumes | BD 3 ml Luer Lock; BD 10 ml; BD Discardit II 20 ml |
| Sterile Gauze Swabs | Cleaning, absorption, dressing changes | 12-ply absorbency, sterile packs, low lint | Sterile Gauze (12-ply) Swab Dressing |
| Gauze Rolls (Than) | Padding, secondary dressings, bulk prep | Cost-efficient roll, easy cutting, broad use | Gauze Than 90 cm × 18 m |
| Catheters (Nelaton) | Intermittent bladder drainage, short procedures | Smooth tip, consistent French sizes | Nel Cath GS 1004 |
| Obstetric — Cord Care | Newborn cord clamping post-delivery | Sterile, positive-lock teeth, secure hold | Umbilical Cord Clamp (Sterile) |
| Gynecology — Karman Cannula | Approved uterine evacuation procedures | Smooth profile, adaptor compatibility, steady seal | Karman-type Cannula with Adaptor (pack) |